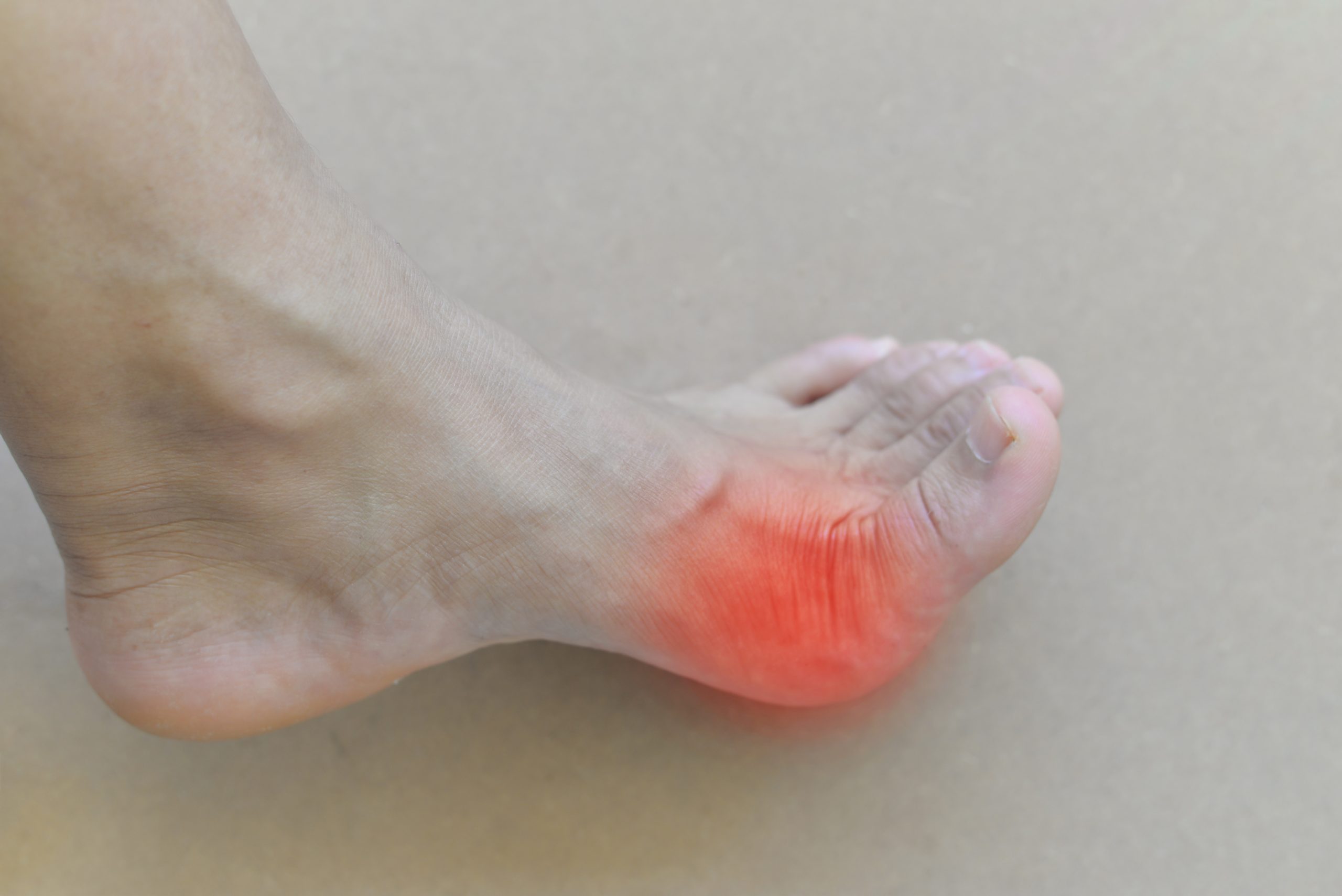
Dealing with gout flare-ups can be challenging, especially when it comes to managing diet and hydration. Choosing the right beverages can significantly impact the severity and frequency of gout attacks. Staying well-hydrated with water is essential, as it helps flush out uric acid from the body.
Certain drinks may also offer additional benefits. Moderate coffee consumption and green tea have been linked to lower uric acid levels, potentially reducing flare-up risks. Additionally, low-fat milk may contribute to uric acid excretion, offering another option for those seeking relief.
Understanding which drinks to incorporate into daily routines can empower individuals with gout to manage their condition more effectively. This article will explore the best drink options that promote health and help alleviate discomfort during flare-ups.
Understanding Gout and Flare-ups
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. When uric acid crystallizes in the joints, it leads to intense pain and swelling. Flare-ups can occur unexpectedly, often affecting a single joint, commonly in the toes.
Common Triggers
Certain factors can trigger a gout flare-up:
- Diet: Foods high in purines, such as red meat and shellfish, can increase uric acid levels.
- Beverages: Alcohol and sugary drinks, particularly those with high-fructose corn syrup, are known to contribute to flare-ups.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can worsen the condition.
Symptoms
During a flare-up, individuals may experience:
- Severe pain in the affected joint
- Swelling and redness
- Difficulty moving the joint
Duration
Without treatment, a gout flare can last from a few days to several weeks. Prompt intervention can significantly reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
Management
Hydration is vital; drinking water helps dilute uric acid levels. Some individuals find that tart cherry juice may provide relief during flare-ups due to its anti-inflammatory properties. Ice application can also alleviate swelling and pain.
Addressing these factors can help manage gout effectively.
Hydration and Gout Management
Proper hydration plays a crucial role in managing gout. It helps to flush uric acid from the body, potentially reducing the frequency of flare-ups.
Recommended Drinks:
- Water: Regular consumption of water is essential. Aim for at least 8 glasses per day to support kidney function.
- Cherry Juice: There is some evidence suggesting that cherry juice may lower uric acid levels. It can be a flavorful option for hydration.
- Coffee: Moderate coffee consumption may have protective effects against gout due to its potential to lower uric acid levels.
Drinks to Avoid:
- Sugary Beverages: Soft drinks containing fructose can increase uric acid levels. These should be limited or avoided.
- Alcohol: Beer and spirits can trigger flare-ups. Limiting alcohol, especially during gout attacks, is recommended.
- High-Purine Juices: Certain fruit juices, particularly those high in fructose, can be detrimental.
Staying hydrated not only aids in managing gout but also promotes overall health. Encouraging a habit of drinking water and other beneficial beverages can significantly improve quality of life for those experiencing gout.
Beneficial Beverages for Gout
Choosing the right beverages can significantly impact gout management. Staying hydrated with specific drinks may help reduce flare-ups and alleviate discomfort. Below are some beneficial options for those experiencing gout.
Water
Water is essential for individuals with gout. It aids in flushing out uric acid, which can crystallize in the joints and lead to painful flare-ups.
- Hydration Goals: Aim for at least 8-10 cups of water daily. Proper hydration can dilute uric acid levels in the bloodstream.
- Impact on Kidney Function: Increased water intake enhances kidney function, allowing for better uric acid excretion.
Drinking plain water or infusing it with lemon can offer additional vitamin C benefits. Lemon water may help neutralize acidity in the body, further supporting uric acid management.
Herbal Teas
Herbal teas provide various benefits for those coping with gout. Certain types can possess anti-inflammatory properties, which may be helpful during flare-ups.
- Nettle Tea: Known for its diuretic properties, nettle tea can aid in eliminating excess uric acid from the body.
- Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants, green tea may help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
Steeping these teas without added sugars enhances their effectiveness. Avoid sweeteners, as sugar can exacerbate gout symptoms.
Coffee
Coffee may also be beneficial for gout sufferers. Research suggests that regular coffee consumption could lower gout risk.
- Uric Acid Reduction: Coffee has been shown to speed up uric acid excretion, potentially lowering blood levels of this compound.
- Two to Three Cups: Aim for two to three cups of coffee daily for favorable effects.
Opt for black coffee or add low-fat milk without sugar. This combination maintains the health benefits without introducing excess calories or sugar.
Dairy Alternatives
Dairy can be a double-edged sword for gout patients. While full-fat dairy may pose risks, certain dairy alternatives might offer benefits.
- Skim Milk: Studies indicate that skim milk can help reduce uric acid levels and mitigate flare-ups.
- Almond or Soy Milk: Dairy alternatives such as almond or soy milk are lower in purine content, making them safer choices.
Choose unsweetened versions to avoid unnecessary sugars. Incorporating these dairy alternatives can enhance dietary variety while supporting gout management.
Dietary Considerations during Flare-ups
During gout flare-ups, dietary choices can significantly influence symptom intensity. Understanding which beverages to avoid or limit is crucial for managing uric acid levels effectively.
Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol plays a significant role in triggering gout flare-ups. Beer, in particular, is high in purines, which can raise uric acid levels and lead to painful attacks. Reducing or eliminating alcohol intake is recommended during flare-ups.
Wine and spirits may appear less problematic, but they still have the potential to exacerbate symptoms. Studies indicate that any form of alcohol can inhibit uric acid excretion, increasing the risk of flare-ups. To minimize discomfort, avoiding all alcoholic beverages during acute episodes is advisable.
Fructose Intake
Fructose, found in many sweetened drinks and juices, is another contributor to increased uric acid production. Sugary beverages, especially those containing high-fructose corn syrup, should be avoided during flare-ups.
Fruit juices, such as apple juice and orange juice, while perceived as healthy, may contain high levels of fructose. Consuming these can lead to raised uric acid levels, potentially sparking a flare-up. It’s critical to limit fructose intake and consider opting for water or unsweetened alternatives to stay hydrated.
Purine-Rich Beverages
In addition to alcohol and fructose, beverages rich in purines can worsen gout symptoms. Some soft drinks, especially those sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup, should be limited or avoided entirely.
Certain energy drinks and protein shakes may also contain high purine levels. Hydration is vital, so focusing on low-purine options like water or herbal teas is best. Keeping uric acid levels in check is essential during flare-ups, and avoiding purine-rich drinks is a key strategy.
Supplements and Natural Remedies
Several supplements and natural remedies may help manage gout flare-ups. These options focus on reducing uric acid levels and inflammation.
Vitamin C: This vitamin may help lower uric acid levels. Increasing vitamin C intake through fruits or supplements can be beneficial.
Cherry Extract: Studies suggest that cherry extract may reduce the frequency of gout attacks. People often find relief from its anti-inflammatory properties.
Bromelain: Found in pineapple, bromelain is another supplement known for its anti-inflammatory effects. Taking bromelain may help reduce gout-related swelling.
Ginger: The anti-inflammatory properties of ginger can assist in pain management during flare-ups. It can be consumed fresh, in teas, or as a supplement.
Lemon Water: Drinking lemon water may help lower uric acid levels. Adding the juice of two lemons to water daily can be an effective remedy.
Bananas: These are low in purines and high in vitamin C. Incorporating bananas into the diet can support lower uric acid production.
Adequate Hydration: Staying hydrated helps flush uric acid from the body. It is recommended to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Incorporating these supplements and remedies into daily routines may offer relief and support during gout flare-ups.
Lifestyle Modifications for Gout Prevention
Managing gout involves adopting specific lifestyle changes to reduce flare-ups. Key modifications include dietary adjustments, hydration, and physical activity.
Hydration:
Staying well-hydrated helps flush uric acid from the body. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily. Other options include:
- Skim milk: May help lower uric acid levels.
- Cherry juice: Some studies suggest it can reduce the frequency of attacks.
Dietary Choices:
Focus on foods that help minimize uric acid levels. Recommended options are:
- Low-fat dairy products: Rich in proteins that don’t increase uric acid.
- Fruits, especially citrus: High in vitamin C, which may help lower uric acid.
Limit High-Purine Foods:
Reduce intake of foods known to be high in purines, including:
- Red meats: Such as beef, lamb, and pork.
- Certain seafood: Including sardines and anchovies.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly lower the risk of gout attacks. Gradual weight loss through a balanced diet is advised.
Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity promotes overall health and can help manage weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
Implementing these lifestyle modifications can contribute to the prevention of gout flare-ups, allowing individuals to manage their condition more effectively.
Medical Treatments for Gout Flare-ups
Managing gout flare-ups often requires targeted medical treatments. These treatments focus on alleviating pain and reducing inflammation.
Medications commonly used include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These provide relief from pain and swelling. Common examples include ibuprofen and naproxen.
- Colchicine: Effective for acute attacks, colchicine can reduce gout-related pain if taken early.
- Corticosteroids: These may be prescribed for severe cases where NSAIDs are ineffective. They help to reduce inflammation quickly.
Long-term management often involves medications that lower uric acid levels. These can prevent future flare-ups by avoiding the formation of uric acid crystals.
- Allopurinol: This medication reduces uric acid production in the body.
- Febuxostat: Another uric acid-lowering option, suitable for individuals who cannot tolerate allopurinol.
In addition to medications, lifestyle changes support treatment efforts. Staying hydrated is crucial, as dehydration can increase uric acid levels. Patients are encouraged to drink plenty of water and limit consumption of sugary beverages.
By combining medication with proper hydration and dietary adjustments, individuals experiencing gout flare-ups can achieve better control over their condition.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
Individuals experiencing a gout flare-up should monitor their symptoms closely. It may be time to seek medical advice if the pain becomes extremely severe or incapacitating.
Swelling around the affected joint that significantly increases or does not improve with home treatment may also warrant a consultation. Persistent redness and warmth around the joint can indicate a worsening condition.
If there are recurrent flare-ups, it is advisable for individuals to assess their uric acid levels. They should consult a healthcare provider if they have not been tested in the last 6 months.
People with accompanying symptoms like fever or chills should not delay in seeking medical attention. These could signal an infection or another underlying issue that requires treatment.
A healthcare provider can also help if self-management strategies, such as dietary changes or over-the-counter medications, fail to provide relief. An evaluation may be necessary to develop a more effective long-term management plan.
For those who have other health conditions, such as kidney disease, early intervention is crucial. This ensures that gout treatment does not conflict with current medications or management plans.